What Is The Meaning Of Vulnerability In Economics Explained
Class 9 Economics Chapter 3 | Vulnerable Groups – Poverty As A Challenge
Keywords searched by users: What is the meaning of vulnerability in economics economic vulnerability example, what is economic vulnerability in disaster, economic vulnerability meaning and example, environmental vulnerability, economic vulnerability synonym, economic vulnerability factors, social vulnerability meaning, economic vulnerability index
What Is Vulnerability In Economics?
In the realm of economics, vulnerability refers to the susceptibility of a country’s economic growth and development to be impeded by unexpected external events, commonly referred to as external shocks (Guillaumont, 2008; 2009). These unforeseen events can encompass a wide range of factors, such as natural disasters, global economic crises, sudden changes in commodity prices, or geopolitical upheavals. Economic vulnerability, therefore, encompasses the capacity of a nation’s economy to withstand and recover from these unexpected challenges, which can have profound implications for its overall well-being, stability, and long-term prosperity. Understanding and assessing economic vulnerability is crucial for policymakers, as it allows them to develop strategies to mitigate risks, enhance resilience, and foster sustainable economic growth.
What Is Economic Vulnerability And Its Example?
Economic vulnerability refers to the precarious financial circumstances that can force families with limited incomes to reside in higher-risk neighborhoods in and around urban areas. These households often face constraints that prevent them from residing in more secure but costlier areas. An illustrative example of economic vulnerability is when families, due to their limited financial resources, find themselves compelled to settle in regions where safety and security may be compromised due to affordability constraints.
What Is Vulnerability Class 9 Economics?
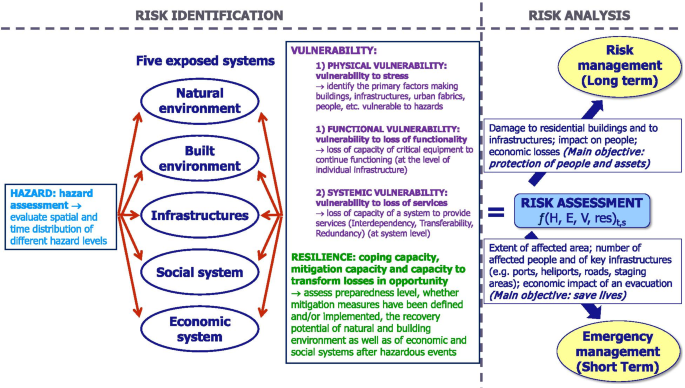
Vulnerability, in the context of Class 9 economics, refers to a set of characteristics influenced by various factors, including physical, social, economic, and environmental elements. These factors or processes collectively heighten the susceptibility of individuals, communities, assets, or systems to the adverse effects of hazards. In Class 9 economics, the study of vulnerability involves examining how these multifaceted aspects contribute to a heightened risk level, thereby deepening our understanding of how different elements can impact economic stability and well-being. This concept allows us to better assess and address vulnerabilities within various economic systems and communities, ultimately facilitating more informed decision-making and policy development.
Collect 32 What is the meaning of vulnerability in economics



Categories: Discover 61 What Is The Meaning Of Vulnerability In Economics
See more here: c1.chewathai27.com

In this paper, economic vulnerability is defined as the exposure of an economy to exogenous shocks, arising out of economic openness, while economic resilience is defined as the policy-induced ability of an economy to withstand or recover from the effects of such shocks.Economic vulnerability can be defined as the likelihood that a country’s economic development process is hindered by the occurrence of exogenous unforeseen events, often called external shocks (Guillaumont, 2008; 2009).Families with low incomes often live in high-risk areas around cities, because they can’t afford to live in safer (and more expensive) places. This is what we call economic vulnerability.
Learn more about the topic What is the meaning of vulnerability in economics.
- Working Paper : Economic Vulnerability and Resilience
- The Economic Vulnerability Index – Ferdi
- What does Vulnerability mean?
- Define vulnerability. How is it determined – Class 9 – EduRev
- Exploring the concept of vulnerability in health care – PMC – NCBI
- Vulnerability and poverty: What are the causes and how are they related
See more: c1.chewathai27.com/category/money-policy