Which Organ Regulates Fish Buoyancy: Unveiling The Mechanism
Science Spotlight: Fish, Swim Bladders And Boyle’S Law
Keywords searched by users: Which organ controls the buoyancy of fish and how does it work how does the swim bladder work, Using the swimbladder as a respiratory organ and or a buoyancy structure benefits and consequences, what is the name of the part of the body that fish use to detect water movement and vibration, Swim bladder, what happens to the swim bladder as a fish moves into deeper water?, Swim bladder disease
Which Organ Controls The Buoyancy Of Fish?
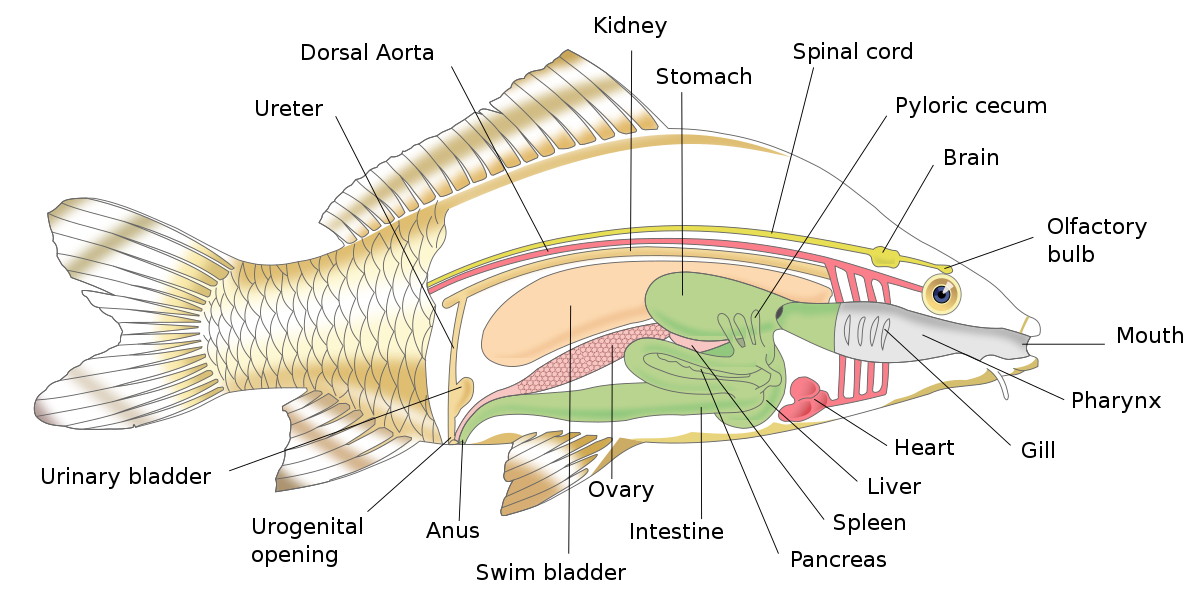
The organ responsible for regulating the buoyancy of fish is known as the swim bladder, which is sometimes referred to as the air bladder. This vital organ is present in the majority of bony fish species. The swim bladder is situated within the body cavity and originates from an extension of the digestive tube. Its primary function is to help fish control their position in the water column by adjusting the amount of gas it contains, allowing them to remain buoyant at various depths. This adaptation enables fish to maintain their desired depth in the water, conserve energy, and efficiently navigate their aquatic environments.
Which Organ Controls The Buoyancy Of Fish And How Does It Work How Does This Organ Differ Between Fish Living Near The Surface And Fish Living At The Bottom?
The swim bladder is a vital organ responsible for regulating the buoyancy of fish. Found in most fish species, this flexible, gas-filled sac is typically located in the dorsal (upper) part of the body cavity. Its primary function is to enable fish to control their position in the water column. Fish, by nature, have a density greater than that of water, which would cause them to sink if not for the swim bladder. When fish cease swimming, the swim bladder plays a crucial role in preventing them from sinking.
However, it’s worth noting that the structure and function of the swim bladder can vary between fish living near the surface and those dwelling at the bottom of the water.
Discover 32 Which organ controls the buoyancy of fish and how does it work





Categories: Found 62 Which Organ Controls The Buoyancy Of Fish And How Does It Work
See more here: c1.chewathai27.com

The trick is the swim bladder, which is basically like an air-inflated balloon that can expand and contract depending on how much gas is inside. When the swim bladder expands it will increase in volume and therefore displace more water. This increases the fish’s buoyancy and it will float upward.swim bladder, also called air bladder, buoyancy organ possessed by most bony fish. The swim bladder is located in the body cavity and is derived from an outpocketing of the digestive tube.Most fish have an organ called the swim bladder. It is a flexible, gas-filled sac located in the dorsal or top portion of the body cavity and helps to control the fish’s buoyancy. Since fish have a density that is heavier than water, they need this swim bladder to not sink when they stop swimming.
Learn more about the topic Which organ controls the buoyancy of fish and how does it work.
- Floating with a Swim Bladder – Scientific American
- Swim bladder | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts
- Fish Dissection Lesson Plan
- Swim Bladder vs. Oily Liver – Catalina Island Marine Institute
- Hawaiʻi Sharks | Skeleton & Buoyancy – Hawaii.gov
- Swim bladder function and buoyancy control in pink snapper (Pagrus …
See more: c1.chewathai27.com/category/money-policy
